The Socket instance
Table of content
Besides emitting and listening to events, the Socket instance has a few attributes that may be of use in your application:
Socket#id
Each new connection is assigned a random 20-characters identifier.
This identifier is synced with the value on the server-side.
Server
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
console.log(socket.id); // x8WIv7-mJelg7on_ALbx
});
Client
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_CONNECT, new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(Object... args) {
System.out.println(socket.id()); // x8WIv7-mJelg7on_ALbx
}
});
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_DISCONNECT, new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(Object... args) {
System.out.println(socket.id()); // null
}
});
Socket#connected
This attribute describes whether the socket is currently connected to the server.
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_CONNECT, new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(Object... args) {
System.out.println(socket.connected()); // true
}
});
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_DISCONNECT, new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(Object... args) {
System.out.println(socket.connected()); // false
}
});
Lifecycle
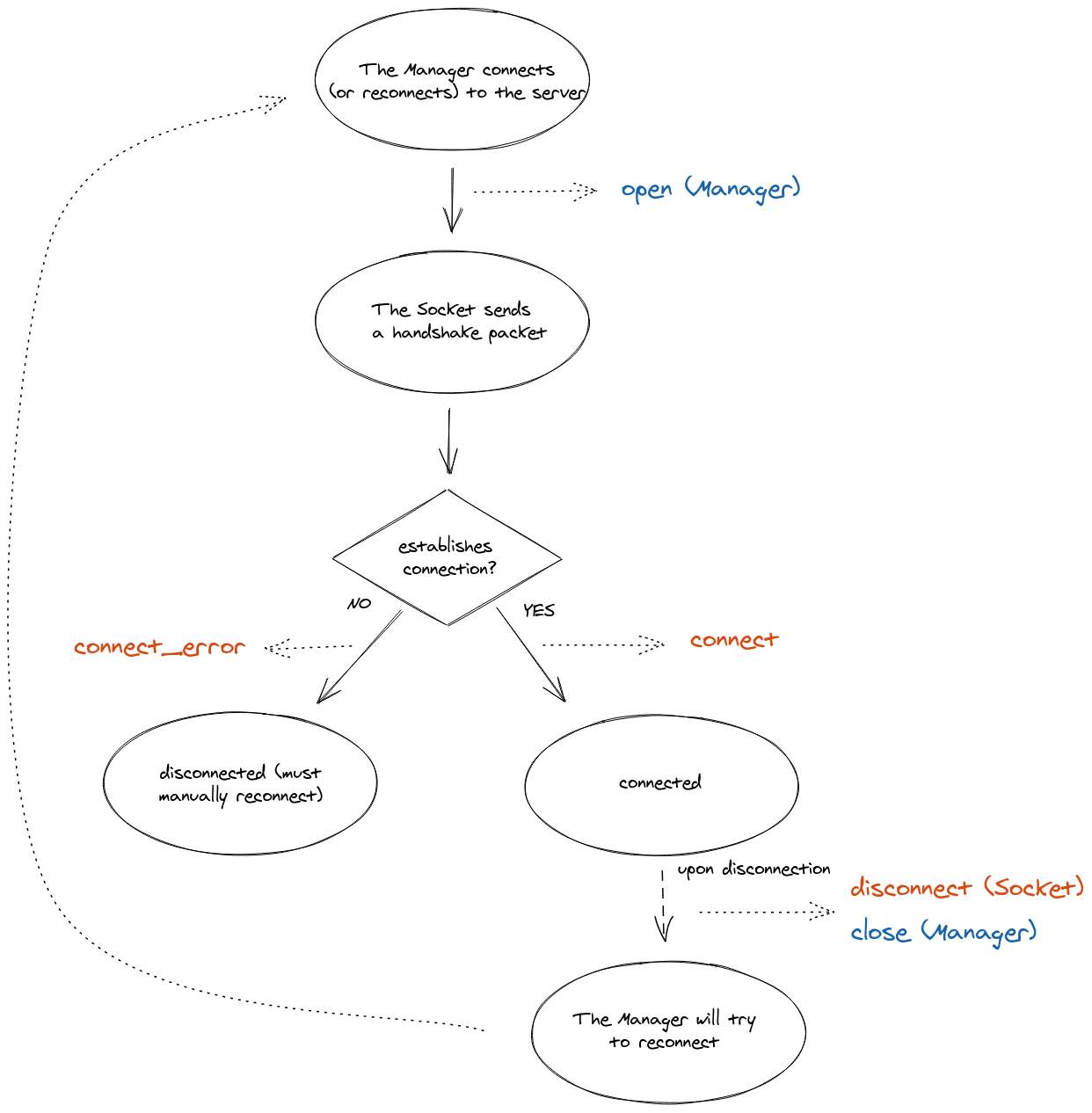
Events
Socket.EVENT_CONNECT
This event is fired by the Socket instance upon connection / reconnection.
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_CONNECT, new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(Object... args) {
// ...
}
});
Please note that you shouldn’t register event handlers in the connect handler itself, as a new handler will be registered every time the Socket reconnects:
// BAD
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_CONNECT, new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(Object... args) {
socket.on("data", new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(Object... args) {
// ...
}
});
}
});
// GOOD
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_CONNECT, new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(Object... args) {
// ...
}
});
socket.on("data", new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(Object... args) {
// ...
}
});
Socket.EVENT_CONNECT_ERROR
This event is fired when the server does not accept the connection (in a middleware function).
You need to manually reconnect. You might need to update the credentials:
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_CONNECT_ERROR, new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(Object... args) {
options.auth.put("authorization", "bearer 1234");
socket.connect();
}
});
Socket.EVENT_DISCONNECT
This event is fired upon disconnection.
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_DISCONNECT, new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(Object... args) {
System.out.println(socket.id()); // null
}
});
Here is the list of possible reasons:
| Reason | Description |
|---|---|
io server disconnect |
The server has forcefully disconnected the socket with socket.disconnect() |
io client disconnect |
The socket was manually disconnected using socket.disconnect() |
ping timeout |
The server did not respond in the pingTimeout range |
transport close |
The connection was closed (example: the user has lost connection, or the network was changed from WiFi to 4G) |
transport error |
The connection has encountered an error (example: the server was killed during a HTTP long-polling cycle) |
Note: those events, along with disconnecting, newListener and removeListener, are special events that shouldn’t be used in your application:
// BAD, will throw an error
socket.emit("disconnect");

